Biology Crossword – Cell biology transport refers to the movement of substances across cell membranes to maintain cellular function and homeostasis. Understanding cell transport is crucial for several reasons, both in basic biological research and practical applications. There is no better way to do it with games like Biology Crossword.
Fundamental Biology
Cell transport processes, such as diffusion, osmosis, and active transport, are essential for maintaining homeostasis within cells. These mechanisms regulate the movement of substances in and out of cells, which is fundamental to cell function and survival.
Health and Disease
Many diseases are linked to defects in cell transport mechanisms. For instance, cystic fibrosis is caused by a malfunction in chloride ion transport, while cancer cells often have altered transport processes that affect drug resistance and growth. Understanding these processes can help in developing targeted treatments and therapies.
Pharmacology
The effectiveness of many drugs depends on their ability to cross cell membranes. Knowledge of cell transport helps in designing drugs that can effectively enter cells or be delivered to specific tissues.
Biotechnology
In fields like genetic engineering and synthetic biology, understanding how substances are transported into and out of cells is key for manipulating cells and developing new technologies.
Cellular Processes
Transport mechanisms are involved in various cellular activities such as nutrient uptake, waste removal, and signal transduction. Grasping these processes helps in understanding how cells interact with their environment and regulate internal activities.
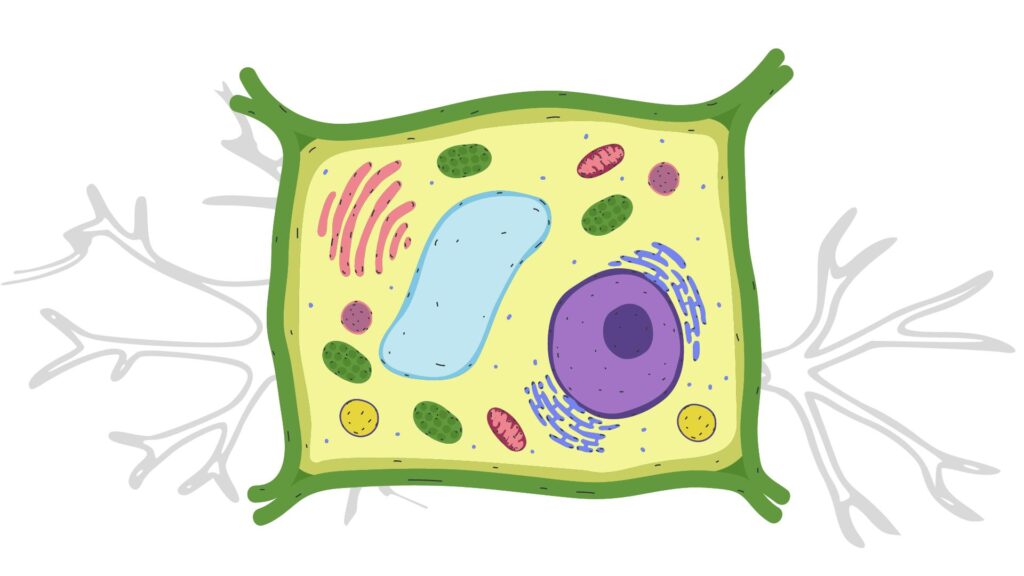
Key components involved in cell transport include:
- Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane): Acts as a selective barrier that regulates the entry and exit of substances through mechanisms like passive and active transport.
- Transport Proteins: Includes channel proteins, carrier proteins, and pumps that facilitate the movement of ions, nutrients, and other molecules across the cell membrane.
- Vesicles: Small membrane-bound sacs that transport materials between different compartments of the cell, such as endosomes and lysosomes.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Involved in the synthesis and initial processing of proteins and lipids, which are then transported to the Golgi apparatus.
- Golgi Apparatus: Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids into vesicles for transport to their final destinations.
- Cytoskeleton: Includes microtubules and actin filaments that provide structural support and serve as tracks for the movement of vesicles and organelles.
- Mitochondria: Produce energy in the form of ATP, which is essential for active transport processes.
- Nuclear Pores: Regulate the transport of molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm, including RNA and proteins.
Overall, learning about cell transport provides insights into how cells function at a fundamental level and can inform a wide range of scientific and medical fields.
Cell Biology Crossword-1
More activities

