Versatility of carbon element and the inception of life on earth
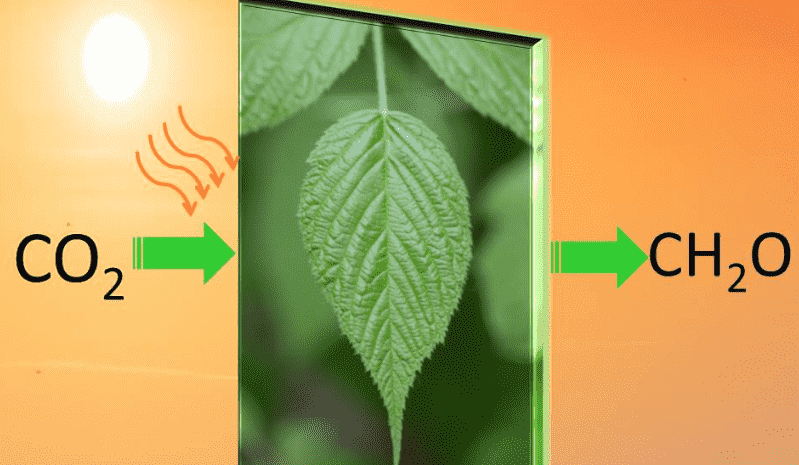
Only about 30 elements participate in all the biological reactions out of 118 elements in the periodic table. Out of these 30 elements >99% weight of the cellular mass is formed of H, O, N and C. Only these selective elements create enormous magic and beautify the mother earth and it is possible because of the peculiar chemical properties of these elements. All the micro and macro structures of the living things are formed from the smaller molecular building blocks which require the carbon as a key element in some or the other way.
Versatility of carbon element and the inception of life on earth Read More »