Spectrophotometer – working principle and solved problems in biology-1
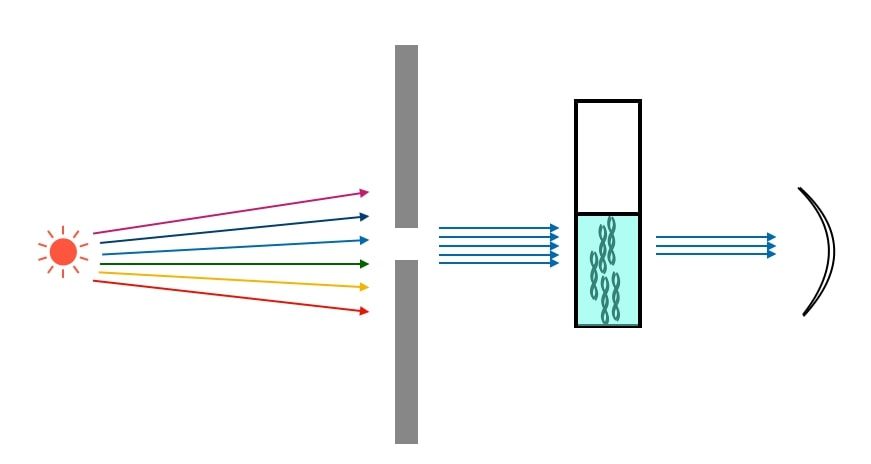
Research in molecular biology has been significantly accelerated by the innovative methodologies of estimation of biomolecules such as spectrophotometer. Therefore it is very much essential to know the quantifiable property of the molecule which can give us numerical value of the amount of the molecules present in the solution and help us in its estimation.
Spectrophotometer – working principle and solved problems in biology-1 Read More »